Page 275 - 360.revista de Alta Velocidad - Nº 5
P. 275
Calculation and rational dimensioning of railway infrastructure materials using numerical modelling
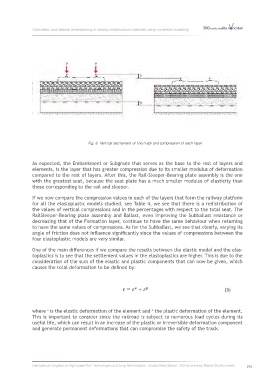
Fig. 6. Vertical settlement of the track and compression of each layer.
As expected, the Embankment or Subgrade that serves as the base to the rest of layers and
elements, is the layer that has greater compression due to its smaller modulus of deformation
compared to the rest of layers. After this, the Rail-Sleeper-Bearing plate assembly is the one
with the greatest seat, because the seat plate has a much smaller modulus of elasticity than
those corresponding to the rail and sleeper.
If we now compare the compression values in each of the layers that form the railway platform
for all the elastoplastic models studied, see Table 4, we see that there is a redistribution of
the values of vertical compressions and in the percentages with respect to the total seat. The
RailSleeper-Bearing plate assembly and Ballast, even improving the Subballast resistance or
decreasing that of the Formation layer, continue to have the same behaviour when returning
to have the same values of compressions. As for the Subballast, we see that clearly, varying its
angle of friction does not influence significantly since the values of compressions between the
four elastoplastic models are very similar.
One of the main differences if we compare the results between the elastic model and the elas-
toplastics is to see that the settlement values in the elastoplastics are higher. This is due to the
consideration of the sum of the elastic and plastic components that can now be given, which
causes the total deformation to be defined by:
where is the elastic deformation of the element and the plastic deformation of the element.
This is important to consider since the railroad is subject to numerous load cycles during its
useful life, which can result in an increase of the plastic or irreversible deformation component
and generate permanent deformations that can compromise the safety of the track.
International Congress on High-speed Rail: Technologies and Long Term Impacts - Ciudad Real (Spain) - 25th anniversary Madrid-Sevilla corridor 273