Page 276 - 360.revista de Alta Velocidad - Nº 5
P. 276
Álvarez, Fernando. Balmaseda, Lucía. Gallego, Inmaculada. Rivas , Ana. Sánchez-Cambronero, San
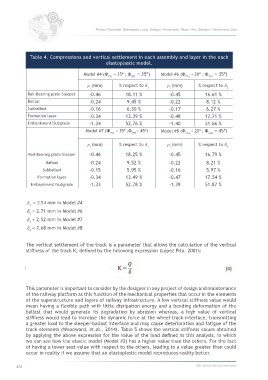
Table 4. Compressions and vertical settlement in each assembly and layer in the each
elastoplastic model.
Model #4 (Φ = 35º ; Φ = 35º) Model #6 (Φ = 20º ; Φ = 35º)
1 1 2 1
(mm) % respect to (mm) % respect to
1 2
Rail-Bearing plate-Sleeper -0.46 18.11 % -0.45 16.61 %
Ballast -0.24 9.45 % -0.22 8.12 %
Subballast -0.16 6.30 % -0.17 6.27 %
Formation layer -0.34 13.39 % -0.48 17.71 %
Embankment/Subgrade -1.34 52.76 % -1.40 51.66 %
Model #7 (Φ = 35º ;Φ = 45º) Model #8 (Φ = 20º ; Φ = 45º)
1 2 2 2
(mm) % respect to (mm) % respect to
1 4
Rail-Bearing plate-Sleeper -0.46 18.25 % -0.45 16.79 %
Ballast -0.24 9.52 % -0.22 8.21 %
Subballast -0.15 5.95 % -0.16 5.97 %
Formation layer -0.34 13.49 % -0.47 17.54 %
Embankment/Subgrade -1.33 52.78 % -1.39 51.87 %
= 2.54 mm in Model #4
1
= 2.71 mm in Model #6
2
= 2.52 mm in Model #7
3
= 2.68 mm in Model #8
4
The vertical settlement of the track is a parameter that allows the calculation of the vertical
stiffness of the track K, defined by the following expression (López Pita. 2001):
This parameter is important to consider by the designer in any project of design and maintenance
of the railway platform as this function of the mechanical properties that occur in the elements
of the superstructure and layers of railway infrastructure. A low vertical stiffness value would
mean having a flexible path with little dissipation energy and a bending deformation of the
ballast that would generate its degradation by abrasion whereas, a high value of vertical
stiffness would lead to increase the dynamic force at the wheel-track interface, transmitting
a greater load to the sleeper-ballast interface and may cause deterioration and fatigue of the
track elements (Woodward, et.al., 2014). Table 5 shows the vertical stiffness values obtained
by applying the above expression for the value of the load defined in this analysis, in which
we can see how the elastic model (Model #2) has a higher value than the others. For the fact
of having a lower seat value with respect to the others, leading to a value greater than could
occur in reality if we assume that an elastoplastic model reproduces reality better.
274 360.revista de alta velocidad