Page 401 - 360.revista de Alta Velocidad - Nº 5
P. 401
Measuring The Long-Term Regional Economic Impacts of High-Speed Rail in China Using a Dynami
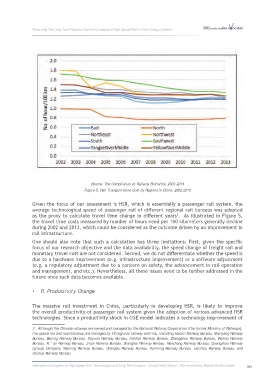
Source: The Compilation of Railway Statistics, 2003-2014
Figure 5. Rail Transportation Cost by Regions in China: 2002-2013
Given the focus of our assessment is HSR, which is essentially a passenger rail system, the
average technological speed of passenger rail of different regional rail bureaus was adopted
3
as the proxy to calculate travel time change in different years . As illustrated in Figure 5,
the travel time costs measured by number of hours need per 100 kilometers generally decline
during 2002 and 2013, which could be considered as the outcome driven by an improvement in
rail infrastructure.
One should also note that such a calculation has three limitations: First, given the specific
focus of our research objective and the data availability, the speed change of freight rail and
monetary travel cost are not considered. Second, we do not differentiate whether the speed is
due to a hardware improvement (e.g. infrastructure improvement) or a software adjustment
(e.g. a regulatory adjustment due to a concern on safety, the advancement in rail operation
and management, and etc.). Nevertheless, all these issues need to be further addressed in the
future once such data becomes available.
• D. Productivity Change
The massive rail investment in China, particularly in developing HSR, is likely to improve
the overall productivity of passenger rail system given the adoption of various advanced HSR
technologies. Since a productivity shock in CGE model indicates a technology improvement of
3 Although the Chinese railways are owned and managed by the National Railway Corporation (the formal Ministry of Railways),
the operation and maintenance are managed by 18 regional railway entities, including Harbin Railway Bureau, Shenyang Railway
Bureau, Beijing Railway Bureau, Taiyuan Railway Bureau, Hohhot Railway Bureau, Zhengzhou Railway Bureau, Wuhan Railway
Bureau, Xi ‘ an Railway Bureau, Jinan Railway Bureau, Shanghai Railway Bureau, Nanchang Railway Bureau, Guangzhou Railway
(group) Company, Nanning Railway Bureau, Chengdu Railway Bureau, Kunming Railway Bureau, Lanzhou Railway Bureau, and
Urumqi Railway Bureau.
International Congress on High-speed Rail: Technologies and Long Term Impacts - Ciudad Real (Spain) - 25th anniversary Madrid-Sevilla corridor 399