Page 396 - 360.revista de Alta Velocidad - Nº 5
P. 396
Zhenhua Chen
4. A Dynamic SCGE Model Approach
The dynamic SCGE model adopted in this study is called dynamic TERM, which stands for
Dynamic The Enormous Regional Model. The model is an essence of the Centre of Policy Studies
(CoPS) at the University of Victoria in Australia and it has been updated by several leading CGE
modelers such as Mark Horridge and Glyn Wittwer. The model has several unique features for a
large-scale multi-regional CGE assessment. For instance, the model has a capacity to achieve a
robust measurement of regional economic impacts given that it is a bottom-up model in which
each region is treated as a separate economy. Such a modeling structure is able to provide a
high degree of regional details, which can make the model to examine the regional impacts
of shocks that may be region-specific. In addition, the model also has a detailed treatment of
transport costs, which can help users better simulate the effects of transportation infrastructure
improvement.
The original TERM is a comparative static model and it was further developed into various
versions for over 13 different countries. The Chinese version of TERM is called SinoTERM, which
is a static model covering 31 provinces and municipalities (Horridge and Wittwer, 2008). The
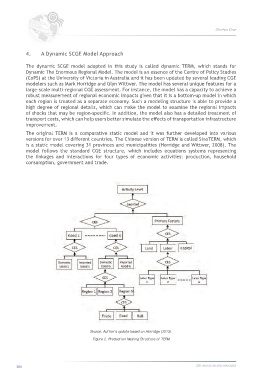
model follows the standard CGE structure, which includes equations systems representing
the linkages and interactions for four types of economic activities: production, household
consumption, government and trade.
Source: Author’s update based on Horridge (2013).
Figure 2. Production Nesting Structure of TERM
394 360.revista de alta velocidad