Page 43 - 360.revista de Alta Velocidad - Nº 6
P. 43
High-speed rail in developing countries and potential inequalities of use: the case of Morocco
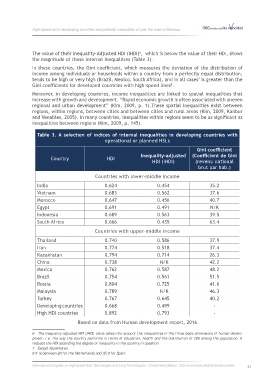
The value of their Inequality‐Adjusted HDI (IHDI) , which is below the value of their HDI, shows
6
the magnitude of these internal inequalities (Table 3).
In these countries, the Gini coefficient, which measures the deviation of the distribution of
income among individuals or households within a country from a perfectly equal distribution,
7
tends to be high or very high (Brazil, Mexico, South Africa), and in all cases is greater than the
8
Gini coefficients for developed countries with high‐speed lines .
Moreover, in developing countries, income inequalities are linked to spatial inequalities that
increase with growth and development. “Rapid economic growth is often associated with uneven
regional and urban development” (Kim, 2009, p. 1).These spatial inequalities exist between
regions, within regions, between cities and between cities and rural areas (Kim, 2009, Kanbur
and Venables, 2005). In many countries, inequalities within regions seem to be as significant as
inequalities between regions (Kim, 2009, p. 145).
Table 3. A selection of indices of internal inequalities in developing countries with
operational or planned HSLs
Gini coefficient
Inequality‐adjusted (Coefficient de Gini
Country HDI
HDI (IHDI) (revenu national
brut par hab.)
Countries with lower‐middle income
India 0.624 0.454 35.2
Vietnam 0.683 0.562 37.6
Morocco 0.647 0.456 40.7
Egypt 0.691 0.491 N/K
Indonesia 0.689 0.563 39.5
South Africa 0.666 0.435 63.4
Countries with upper‐middle income
Thailand 0.740 0.586 37.9
Iran 0.774 0.518 37.4
Kazakhstan 0.794 0.714 26.3
China 0.738 N/K 42.2
Mexico 0.762 0.587 48.2
Brazil 0.754 0.561 51.5
Russia 0.804 0.725 41.6
Malaysia 0.789 N/K 46.3
Turkey 0.767 0.645 40.2
Developing countries 0.668 0.499 ‐
High HDI countries 0.892 0.793 ‐
Based on data from Human development report, 2016
6 The inequality‐adjusted HDI (IHDI) value takes into account the inequalities in the three basic dimensions of human develo‐
pment, i.e. the way the country performs in terms of education, health and the distribution of GNI among the population. It
reduces the HDI according the degree of inequality in the country in question.
7 Except Kazakhstan.
8 It is between 28 for the Netherlands and 35.9 for Spain.
International Congress on High-speed Rail: Technologies and Long Term Impacts - Ciudad Real (Spain) - 25th anniversary Madrid-Sevilla corridor 41