Page 321 - 360.revista de Alta Velocidad - Nº 6
P. 321
Regional diffusion and adoption effects on HSR demand expansion
accessibility to HSR station close to city center have a strong Adoption Effects. Instead, the higher
the supply of road network, the lower the value of Adoption Effects. This illustrates that cars are
the competitive transport mode of high-speed railway in Taiwan due to country size. Among the
explanatory variables, the variable which has the greatest influence on Adoption Effects is aging.
The proportion of the elderly population has a negative impact on the level of Adoption Effects.
Table 3. Model estimation results
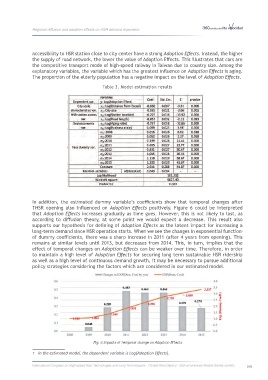
In addition, the estimated dummy variable’s coefficients show that temporal changes after
THSR opening also influenced on Adoption Effects positively. Figure 6 could be interpreted
that Adoption Effects increases gradually as time goes. However, this is not likely to last, as
according to diffusion theory, at some point we would expect a decrease. This result also
supports our hypothesis for defining of Adoption Effects as the latent impact for increasing a
1
long-term demand since HSR operation starts. When we see the changes in exponential function
of dummy coefficients, there was a sharp increase in 2011 (after 4 years from opening). This
remains at similar levels until 2013, but decreases from 2014. This, in turn, implies that the
effect of temporal changes on Adoption Effects can be weaker over time. Therefore, in order
to maintain a high level of Adoption Effects for securing long term sustainable HSR ridership
as well as a high level of continuous demand growth, it may be necessary to pursue additional
policy strategies considering the factors which are considered in our estimated model.
Fig. 6 Impacts of temporal change on Adoption Effects
1 In the estimated model, the dependent variable is Log(Adoption Effects).
International Congress on High-speed Rail: Technologies and Long Term Impacts - Ciudad Real (Spain) - 25th anniversary Madrid-Sevilla corridor 319