Page 320 - 360.revista de Alta Velocidad - Nº 6
P. 320
Kim, Junghwa. Schmöcker, Jan-Dirk. Li, Yeun-Touh. Demizu, Fumiaki.
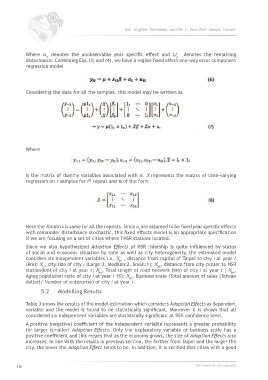
Where α denotes the unobservable year specific effect and U denotes the remaining
it
it
disturbance. Combining Eqs.(3) and (4), we have a region-fixed effect one-way error component
regression model
Considering the data for all the samples, this model may be written as
Where
is the matrix of dummy variables associated with α. X represents the matrix of time-varying
regressors on t samples for i repeat and is of the form
th
Here the X matrix is same for all the repeats. Since α are assumed to be fixed year specific effects
t
with remainder disturbance stochastic, this fixed effects model is an appropriate specification
if we are focusing on a set of cities where THSR stations located.
Since we also hypothesized Adoption Effects of HSR ridership is quite influenced by status
of social and economic situation by time as well as city heterogeneity, the estimated model
considers six independent variables i.e. X , distance from capital of Taipei to city i at year t
1it
(km); X , city size of city i (Large:3, Medium:2, Small:1); X , distance from city center to HSR
2i
3it
station(km) of city i at year t; X , Total length of road network (km) of city i at year t ; X ,
5it
4it
Aging population ratio of city i at year t (%); X , Business scale (Total amount of sales (Taiwan
6it
dollar)/ Number of enterprise) of city i at year t.
5.2 Modelling Results
Table 3 shows the results of the model estimation which considers Adoption Effects as dependent
variable and the model is found to be statistically significant. Moreover it is shown that all
considered six independent variables are statistically significant at 95% confidence level.
A positive (negative) coefficient of the independent variable represents a greater probability
for larger (smaller) Adoption Effects. Only the explanatory variable of business scale has a
positive coefficient and this means that as the economy grows, the size of Adoption Effects also
increases. In line with the results in previous section, the farther from Taipei and the larger the
city, the lower the Adoption Effect tends to be. In addition, it is verified that cities with a good
318 360.revista de alta velocidad