Page 319 - 360.revista de Alta Velocidad - Nº 6
P. 319
Regional diffusion and adoption effects on HSR demand expansion
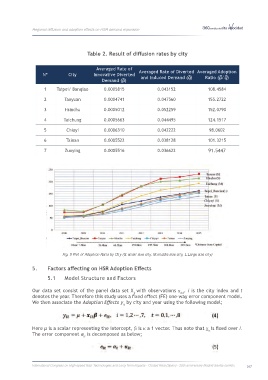
Table 2. Result of diffusion rates by city
Averaged Rate of Averaged Rate of Diverted Averaged Adoption
− −
Nº City Innovative Diverted and Induced Demand (q) Ratio (p/q)
−
−
Demand (p)
1 Taipei/ Banqiao 0.0005815 0.043152 108.4584
2 Taoyuan 0.0004741 0.047560 155.2722
3 Hsinchu 0.0005012 0.052259 152.0790
4 Taichung 0.0005663 0.044495 124.1517
5 Chiayi 0.0006310 0.042222 98.0602
6 Tainan 0.0005522 0.038128 101.3215
7 Zuoying 0.0005516 0.036622 91.5447
Fig. 5 Plot of Adoption Ratio by City (S: small sixe city, M:middle size city, L:Large size city)
5. Factors affecting on HSR Adoption Effects
5.1 Model Structure and Factors
Our data set consist of the panel data set X with observations x . i is the city index and t
k
itk
denotes the year. Therefore this study uses a fixed effect (FE) one-way error component model.
We then associate the Adoption Effects y by city and year using the following model;
it
Here μ is a scalar representing the intercept, β is κ a 1 vector. Thus note that χ is fixed over i.
it
The error component e is decomposed as below;
it
International Congress on High-speed Rail: Technologies and Long Term Impacts - Ciudad Real (Spain) - 25th anniversary Madrid-Sevilla corridor 317