Page 412 - 360.revista de Alta Velocidad - Nº 5
P. 412
Dalkic, Gulcin. Tuydes-Yaman, Hediye. Delaplace, Marie.
1. Introduction
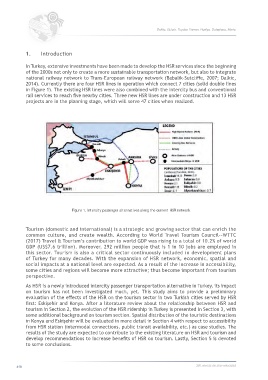
In Turkey, extensive investments have been made to develop the HSR services since the beginning
of the 2000s not only to create a more sustainable transportation network, but also to integrate
national railway network to Trans-European railway network (Babalik-Sutcliffe, 2007; Dalkic,
2014). Currently there are four HSR lines in operation which connect 7 cities (solid double lines
in Figure 1). The existing HSR lines were also combined with the intercity bus and conventional
rail services to reach five nearby cities. Three new HSR lines are under construction and 13 HSR
projects are in the planning stage, which will serve 47 cities when realized.
Figure 1. Intercity passenger alternatives along the current HSR network
Tourism (domestic and international) is a strategic and growing sector that can enrich the
common culture, and create wealth. According to World Travel Tourism Council--WTTC
(2017) Travel & Tourism’s contribution to world GDP was rising to a total of 10.2% of world
GDP (US$7.6 trillion). Moreover, 292 million people that is 1 in 10 jobs are employed in
this sector. Tourism is also a critical sector continuously included in development plans
of Turkey for many decades. With the expansion of HSR network, economic, spatial and
social impacts at a national level are expected. As a result of the increase in accessibility,
some cities and regions will become more attractive; thus become important from tourism
perspective.
As HSR is a newly introduced intercity passenger transportation alternative in Turkey, its impact
on tourism has not been investigated much, yet. This study aims to provide a preliminary
evaluation of the effects of the HSR on the tourism sector in two Turkish cities served by HSR
first: Eskişehir and Konya. After a literature review about the relationship between HSR and
tourism in Section 2, the evolution of the HSR ridership in Turkey is presented in Section 3, with
some additional background on tourism section. Spatial distribution of the touristic destinations
in Konya and Eskişehir will be evaluated in more detail in Section 4 with respect to accessibility
from HSR station (intermodal connections, public transit availability, etc.) as case studies. The
results of the study are expected to contribute to the existing literature on HSR and tourism and
develop recommendations to increase benefits of HSR on tourism. Lastly, Section 5 is devoted
to some conclusions.
410 360.revista de alta velocidad