Page 388 - 360.revista de Alta Velocidad - Nº 5
P. 388
Zhenhua Chen
1. Introduction
Rail infrastructure system in China has experienced an exponential expansion over the past
decade due to a strong support from the central government. As illustrated in Table 1, the
National Development and Reform Commission of China has launched three consecutive
planning strategies for mid- and long-term rail network development in 2004, 2008 and
2016, respectively, to promote a continuous development of a nationwide rail infrastructure
network. These strategies outline both high-level national and regional planning goals and
objectives in terms of scale and technological specifications. Hence, they provide a clear
guidance to rail industries and local governments for rail infrastructure development. One
major highlight of these strategies is the development of an interconnected high-speed rail
(HSR) networks to facilitate intercity passenger travel. These HSR systems are expected to
be more advanced than conventional passenger rail because most trainsets have a capacity of
running at 250 km/h or above given the introduction of Electric Multiple Units (EMUs) and the
design of passenger dedicated lines (PDL). In addition to the benefits of a higher speed, the
HSR systems also provide better travel experience than conventional rail service in terms of
on-time performance, comfort, safety and service frequency (Givoni and Banister, 2012). The
systems are also expected to alleviate the conflict between demand and supply for both freight
and passenger rail transport (Chen and Haynes, 2015).
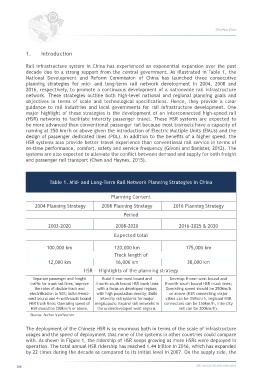
Table 1. Mid- and Long-Term Rail Network Planning Strategies in China
Planning Content
2004 Planning Strategy 2008 Planning Strategy 2016 Planning Strategy
Period
2003-2020 2008-2020 2016-2025 & 2030
Expected total
100,000 km 120,000 km 175,000 km
Track length of
12,000 km 16,000 km 38,000 km
HSR - Highlights of the planning strategy
Separate passenger and freight Build 4-east-west bound and Develop 8-east-west bound and
traffic for trunk rail lines; Improve 4-north-south bound HSR trunk lines 8-north-south bound HSR trunk lines;
the rates of double-track and with a focus on developed regions Operating speed should be 250km/h
electrification to 50%; build 4-east- with high population density; Build or above (HSR connecting major
west bound and 4-north-south bound intercity rail systems for major cities can be 350km/h, regional HSR
HSR trunk lines; Operating speed of megalopolis; Expand rail networks in connectors can be 250km/h, intercity
HSR should be 200km/h or above. the underdeveloped west regions. rail can be 200km/h).
Source: Author’s collection.
The deployment of the Chinese HSR is so enormous both in terms of the scale of infrastructure
usages and the speed of deployment that none of the systems in other countries could compare
with. As shown in Figure 1, the ridership of HSR keeps growing as more HSRs were deployed in
operation. The total annual HSR ridership has reached 1.44 billion in 2016, which has expanded
by 22 times during the decade as compared to its initial level in 2007. On the supply side, the
386 360.revista de alta velocidad