Page 145 - 360.revista de Alta Velocidad - Nº 5
P. 145
Probabilistic Safety Analysis of High Speed and Conventional Railway Lines
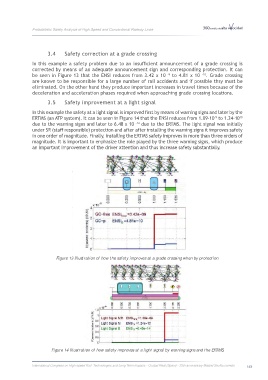
3.4 Safety correction at a grade crossing
In this example a safety problem due to an insufficient announcement of a grade crossing is
corrected by means of an adequate announcement sign and corresponding protection. It can
be seen in Figure 13 that the ENSI reduces from 3.42 x 10 to 4.81 x 10 . Grade crossing
-10
-9
are known to be responsible for a large number of rail accidents and if possible thsy must be
eliminated. On the other hand they produce important increases in travel times because of the
deceleration and acceleration phases required when approaching grade crossing locations.
3.5 Safety improvement at a light signal
In this example the safety at a light signal is improved first by means of warning signs and later by the
ERTMS (an ATP system). It can be seen in Figure 14 that the ENSI reduces from 1.09·10 to 1.24·10
-10
-9
due to the warning signs and later to 6.48 x 10 due to the ERTMS. The light signal was initially
-14
under SR (staff responsible) protection and after after installing the warning signs it improves safety
in one order of magnitude. Finally, installing the ERTMS safety improves in more than three orders of
magnitude. It is important to enphasize the role played by the three warning signs, which produce
an important improvement of the driver attention and thus increase safety substantially.
Figure 13 Illustration of how the safety improves at a grade crossing when by protection.
Figure 14 Illustration of how safety improves at a light signal by warning signs and the ERTMS.
International Congress on High-speed Rail: Technologies and Long Term Impacts - Ciudad Real (Spain) - 25th anniversary Madrid-Sevilla corridor 143