Page 526 - 360.revista de Alta Velocidad - Nº 6
P. 526
Ortega, Alejandro. Almujibah, Hamad. Preston, John.
and Madrid – Valencia 14% (PWC, 2010). The remaining demand can be attributed to transport
mode shift. There are also important differences between induced traffic expectations and
reality that can be explained by higher prices and lower frequencies than forecasted as well
as economic downturn (Fernandez, 2012). In fact, as Fernandez pointed out official forecasts
were revised downwards before the new lines entered into service to take into account the
new services and prices. So, forecasting HSR demand accurately is difficult (Guirao and Campa,
2014) and therefore there are usually implicit risks associated with demand. Moreover, official
forecasts could also be deliberately biased upwards due to strategic misrepresentation from
the Government (van Wee and Flyvbjerg, 2010); they can justify potential demand in the future
to develop HSR.
By contrast, domestic transport in Saudi Arabia is composed of three main modes: road, air
and marine. Despite the recent increase in air transport demand, road transport has the lion’s
share of the transport in Saudi Arabia by far, with more than 95% of the national passenger-km.
This high percentage can be explained by the easy accessibility to private automobiles as well
as low fuel prices, which have increased automobile traffic levels in recent years resulting in
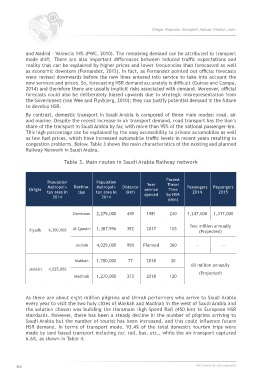
congestion problems. Below, Table 3 shows the main characteristics of the existing and planned
Railway Network in Saudi Arabia.
Table 3. Main routes in Saudi Arabia Railway network
Fastest
Population Population Year Travel
Origin Metropoli- Destina- Metropoli- Distance service Time Passengers Passengers
tan area in tion tan area in (km) opened by HSR 2014 2015
2014 2014
(min)
Dammam 2,275,000 449 1981 240 1,247,000 1,317,000
Two million annually
Riyadh 6,300,000 Al-Qassim 1,387,996 352 2017 105 (Projected)
Jeddah 4,025,000 950 Planned 360 -- --
Makkah 1,780,000 77 2018 30
60 million annually
Jeddah 4,025,000
(Projected)
Madinah 1,270,000 373 2018 120
As there are about eight million pilgrims and Umrah performers who arrive to Saudi Arabia
every year to visit the two holy cities of Makkah and Madinah in the west of Saudi Arabia and
the solution chosen was building the Haramain High Speed Rail (450 km) to European HSR
standards. However, there has been a steady decline in the number of pilgrims arriving to
Saudi Arabia but the number of tourist has been increased, and this could influence future
HSR demand. In terms of transport mode, 93.4% of the total domestic tourism trips were
made by land based transport including car, rail, bus, etc., while the air transport captured
6.6%, as shown in Table 4.
524 360.revista de alta velocidad