Page 380 - 360.revista de Alta Velocidad - Nº 5
P. 380
Pagliara, Francesca. Menicocci, Fabrizio.Vassallo, José Manuel. Gómez Sánchez, Juan.
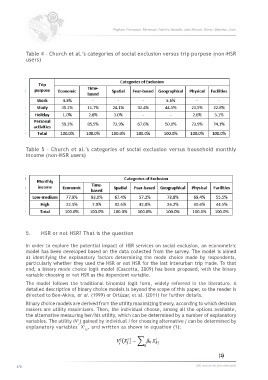
Table 4 – Church et al.’s categories of social exclusion versus trip purpose (non-HSR
users)
Table 5 – Church et al.’s categories of social exclusion versus household monthly
income (non-HSR users)
5. HSR or not HSR? That is the question
In order to explore the potential impact of HSR services on social exclusion, an econometric
model has been developed based on the data collected from the survey. The model is aimed
at identifying the explanatory factors determining the mode choice made by respondents,
particularly whether they used the HSR or not HSR for the last interurban trip made. To that
end, a binary mode choice logit model (Cascetta, 2009) has been proposed, with the binary
variable choosing or not HSR as the dependent variable.
The model follows the traditional binomial logit form, widely referred in the literature. A
detailed description of binary choice models is beyond the scope of this paper, so the reader is
directed to Ben-Akiva, et al. (1999) or Ortúzar, et al. (2011) for further details.
Binary choice models are derived from the utility maximizing theory, according to which decision
makers are utility maximizers. Then, the individual choose, among all the options available,
the alternative measuring her/his utility, which can be determined by a number of explanatory
variables. The utility (V ) gained by individual i for choosing alternative j can be determined by
i
j
explanatory variables X , and written as shown in equation (1):
i
kj
378 360.revista de alta velocidad