
Categories
Publications
Bayesian Railway Localization System Based on Raw GNSS Measurements and Inertial Sensors
29/4/2015
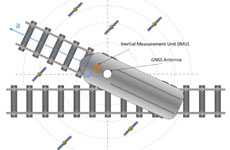
Current railway localization systems rely on both track side and train side sensors, providing only a discrete positioning of the trains at a high cost in deployment and maintenance. On the other hand, Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) can provide a world-wide positioning at a lower cost since it requires only an antenna and a receiver on board. However, due to disadvantageous environments, the GNSS signals may get blocked and the use of additional sensor and information of the railway map is necessary to achieve a robust positioning. In this article, we propose a probabilistic localization system for trains using raw measurements from GNSS, inertial sensors and a digital railway map. The combination of these sensors in our algorithm can achieve a robust localization even in low visibility situations.
Download paper »


