Page 244 - 360.revista de Alta Velocidad - Nº 5
P. 244
López-Bachiller Fernández, Miguel. Sampedro Rodríguez, Ángel. Díaz Minguela, Jesús.
5. Potentially adverse factors
Three are the aspects which most negatively influence soil stabilization: its content in organic
material, the soluble sulphates and the soils particles bigger than 80 mm.
• The content in organic matter can inhibit the Pozzolanic reactions and retarder the effects
of the binder on the ground. In case of soils with excessive rates of this, you should conduct
studies seeing the evolution of the improvement to more long‐term than usual, to dose
correctly the necessary binder (lime can remove part of this organic matter).
• The content of soluble sulphates can form ettringite (trisulfoaluminato calcium) and other
similar substances (thaumasite) produced by the soil and lime in a Pozzolanic reaction. They
are very expansive and it can break the already mixed and compacted layers. The content
of soluble sulphates can exist in the soil, or can be provided by existing groundwater that
can affect stabilization through the reaction of sulphates solubilized in water with calcium
aluminates hydrated.
Lime needed for this reaction can come from lime added when this is used as a stabilizing
agent, or from cement when it is released in the process of setting and curing.
The use of sulfo‐resistent cements does not exempt from the attention that must be paid in
the works in which appear the sulfates. Normally cements that resist the attack of sulfur
have a low content on alumina, therefore avoiding the formation of the product S ‐ Al ‐ Ca,
whose stable form can contain up to 24 water molecules. However, in soil stabilization may
be sufficient alumina content to form part of the damaging formula.
• The presence of big amount of big stones (bigger than 80‐100 mm), especially if there is
no continuous soil grading, makes impossible to achieve a good mixture and can cause
problems in the machine.
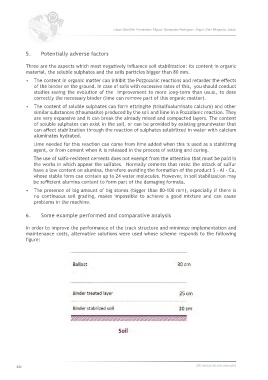
6. Some example performed and comparative analysis
In order to improve the performance of the track structure and minimize implementation and
maintenance costs, alternative solutions were used whose scheme responds to the following
figure:
242 360.revista de alta velocidad