Page 379 - 360.revista de Alta Velocidad - Nº 6
P. 379
The configurations of Chinese national urban systems in both high-speed railway and airline networks
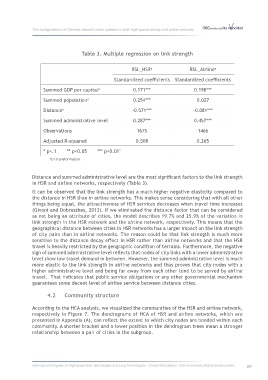
Table 3. Multiple regression on link strength
RSL_HSR RSL_Airline
a
a
Standardized coefficients Standardized coefficients
a
Summed GDP per capital 0.171*** 0.198***
Summed population 0.254*** 0.027
a
Distance -0.571*** -0.081***
a
Summed administrative level 0.287*** 0.457***
Observations 1675 1466
Adjusted R-squared 0.508 0.265
* p<.1 ** p<0.05 *** p<0.01"
a Ln transformation.
Distance and summed administrative level are the most significant factors to the link strength
in HSR and airline networks, respectively (Table 3).
It can be observed that the link strength has a much higher negative elasticity compared to
the distance in HSR than in airline networks. This makes sense considering that with all other
things being equal, the attractiveness of HSR services decreases when travel time increases
(Givoni and Dobruszkes, 2013). If we eliminated the distance factor that can be considered
as not being an attribute of cities, the model describes 19.7% and 25.9% of the variation in
link strength in the HSR network and the airline network, respectively. This means that the
geographical distance between cities in HSR networks has a larger impact on the link strength
of city pairs than in airline networks. The reason could be that link strength is much more
sensitive to the distance decay effect in HSR rather than airline networks and that the HSR
travel is heavily restricted by the geographic condition of terrains. Furthermore, the negative
sign of summed administrative level reflects that nodes of city links with a lower administrative
level show low travel demand in between. However, the summed administrative level is much
more elastic to the link strength in airline networks and thus proves that city nodes with a
higher administrative level and being far away from each other tend to be served by airline
travel. That indicates that public service obligations or any other governmental mechanism
guarantees some decent level of airline service between distance cities.
4.2 Community structure
According to the HCA analysis, we visualized the communities of the HSR and airline network,
respectively in Figure 7. The dendrograms of HCA of HSR and airline networks, which are
presented in Appendix (A), can reflect the extent to which city nodes are bonded within each
community. A shorter bracket and a lower position in the dendrogram trees mean a stronger
relationship between a pair of cities in the subgroup.
International Congress on High-speed Rail: Technologies and Long Term Impacts - Ciudad Real (Spain) - 25th anniversary Madrid-Sevilla corridor 377