Page 157 - 360.revista de Alta Velocidad - Nº 5
P. 157
Precise and reliable localization as a core of railway automation (Rail 4.0)
to show the interdependencies between the technological or procedural developments and
the high level KPIs of the railway system. The overall objective is to prove the achievement
of the objectives of Shift2Rail by determining to which extend the aims of reducing costs and
improving availability and capacity will be reached. In a first step, these interdependencies will
be analysed as cause-and-effect chains in order to obtain a qualitative model. Subsequently,
the qualitative relations will be replaced by mathematical and logical descriptions. This is
necessary in order to apply the model to data of the different market segments like high speed,
regional, urban / suburban and freight rail. The analysis of the interdependencies as well as
the application of the model is done in close collaboration between industry, infrastructure
managers, railway operators and scientific institutions. Thus a KPI model will be generated
which covers all aspects of the entire railway system. The presentation will cover the approach
that has been chosen to develop the qualitative and quantitative model, share the experience
made during this process and show the first results of the impact assessment of the Joint
Undertaking Shift2Rail.
4. Impact on the Competitiveness of the European railway systems
The introduction of GNSS in the rail domain is now recognized as a powerful tool for ERTMS
deployment, old system renewal. A study performed by Bocconi University for the ERSAT EAV
projects shows that GNSS-based ERTMS proves to be especially convenient because of relevant
savings in operating expenses: -67% each year compared to the traditional ERTMS [Galileo
Services, 2016]. Moreover, the cost/benefit ratio will be maximized if satcoms are integrated
in the global system.
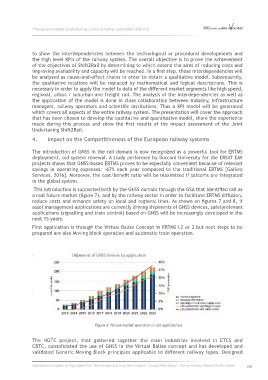
This introduction is supported both by the GNSS domain through the GSA that identified rail as
a real future market (figure 7), and by the railway sector in order to facilitate ERTMS diffusion,
reduce costs and enhance safety on local and regional lines. As shown on figures 7 and 8, if
asset management applications are currently driving shipments of GNSS devices, safetyrelevant
applications (signalling and train control) based on GNSS will be increasingly developed in the
next 15 years.
First application is through the Virtual Balise Concept in ERTMS L2 or 3 but next steps to be
prepared are also Moving block operation and automatic train operation.
Figure 3: Future market evolution in rail applications
The NGTC project, that gathered together the main industries involved in ETCS and
CBTC, consolidated the use of GNSS in the Virtual Balise concept and has developed and
validated Generic Moving Block principles applicable to different railway types. Designed
International Congress on High-speed Rail: Technologies and Long Term Impacts - Ciudad Real (Spain) - 25th anniversary Madrid-Sevilla corridor 155