
Categorías
Publicaciones
Development of an alternative maintenance technique for railway ballasted tracks
28/6/2018
Currently, ballast tamping is the most common maintenance intervention in ballasted tracks in order to restore original geometry while recovering damping capacity. However, it is wellknown the limited effectiveness of this technique due to the degradation of ballast particles during tamping, and to the memory phenomenon of ballast layer which quickly restores its pre-maintenance geometry.
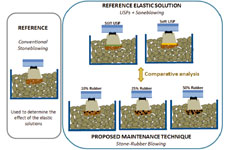
Then, under the need for developing more durable and effective maintenance techniques, this paper proposes an alternative process based on combining the benefits of using Under-Sleeper Pads and the process known as Stoneblowing, by replacing part of the small stones applied during this last technique with rubber particles from wasted tires that act as flexible aggregates under the sleeper. For this purpose, this paper presents an initial laboratory study focused on analysing the viability and effectiveness of this alternative technique while defining the influence of the quantity of rubber as main designing parameter. Results are based on full-scale testing box tests, and they show that this process allows for reducing short and long-term ballast settlement while reducing ballast degradation and the stress transmitted to sub-layers, in comparison to conventional stoneblowing and to the use of under-sleeper pads. Also, it is possible to optimize track deflection and damping capacity by using different quantities of rubber.
Descargar artículo (pdf) »


